Amputation and the Critical Role of Compression Therapy for Diabetic Patients
Understanding Diabetic Amputations: A Growing Concern
Diabetes, a chronic condition affecting millions worldwide, can lead to a range of severe complications if not properly managed. One of the most devastating is the risk of amputation, particularly of the lower limbs. Diabetic neuropathy (nerve damage) and peripheral artery disease (poor circulation) can significantly impair sensation and blood flow in the feet and legs, making them highly susceptible to ulcers, infections, and gangrene. When these conditions become untreatable, amputation may be a necessary, life-saving measure.
The journey after a diabetic amputation is multifaceted, involving physical recovery, emotional adjustment, and learning to adapt to a new way of life. While the initial surgical procedure is crucial, post-operative care and long-term management are equally vital for successful rehabilitation and improved quality of life.

The Power of Compression Therapy: A Post-Amputation Essential
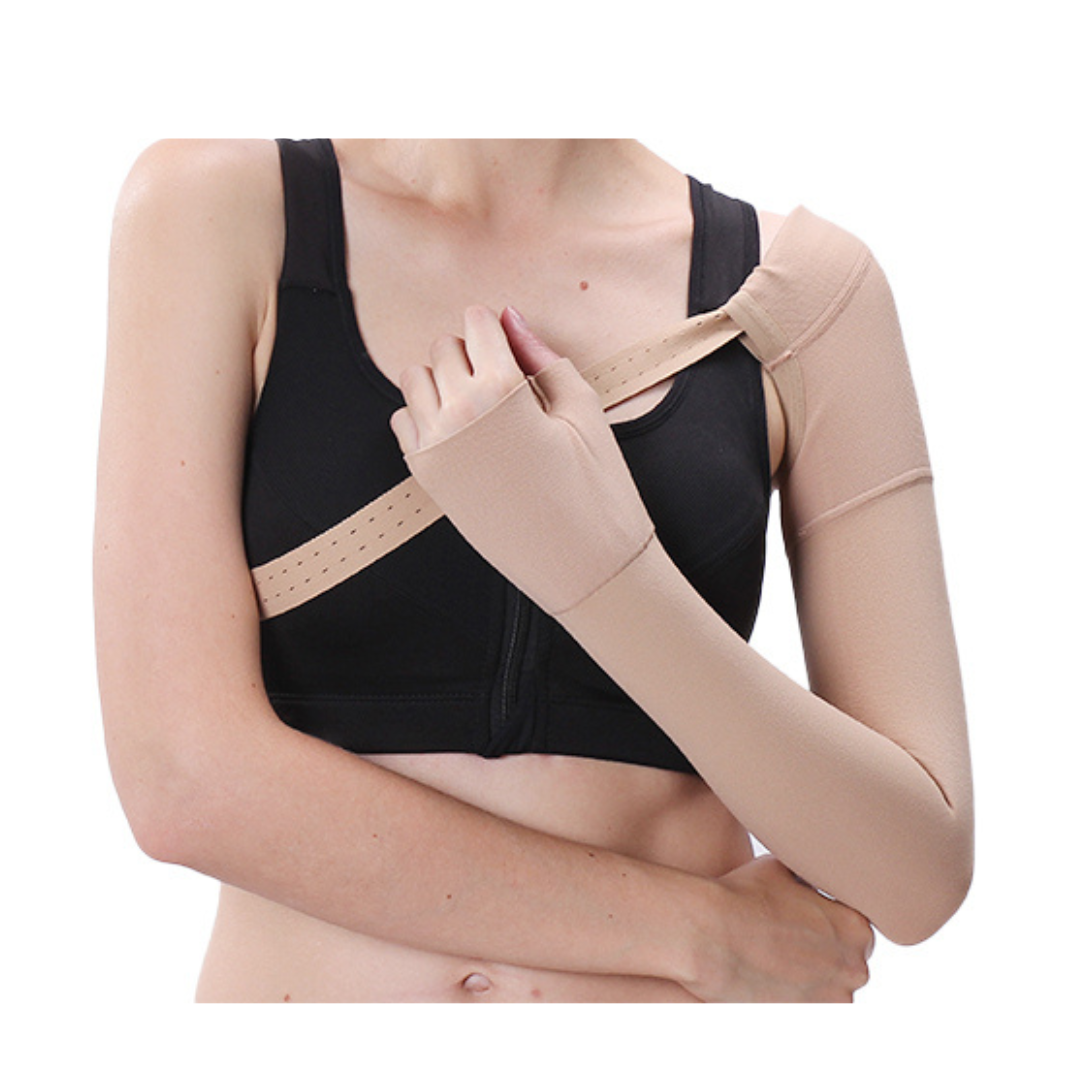
Among the various strategies for managing an amputated limb, compression therapy stands out as a fundamental and highly effective component, especially for diabetic patients. Compression therapy involves applying controlled pressure to the residual limb (stump) using specialized garments like stump shrinkers, compression stockings, or wraps. Its benefits are extensive and directly address common challenges faced by amputees.
Key Benefits of Compression Therapy for Amputees:
-
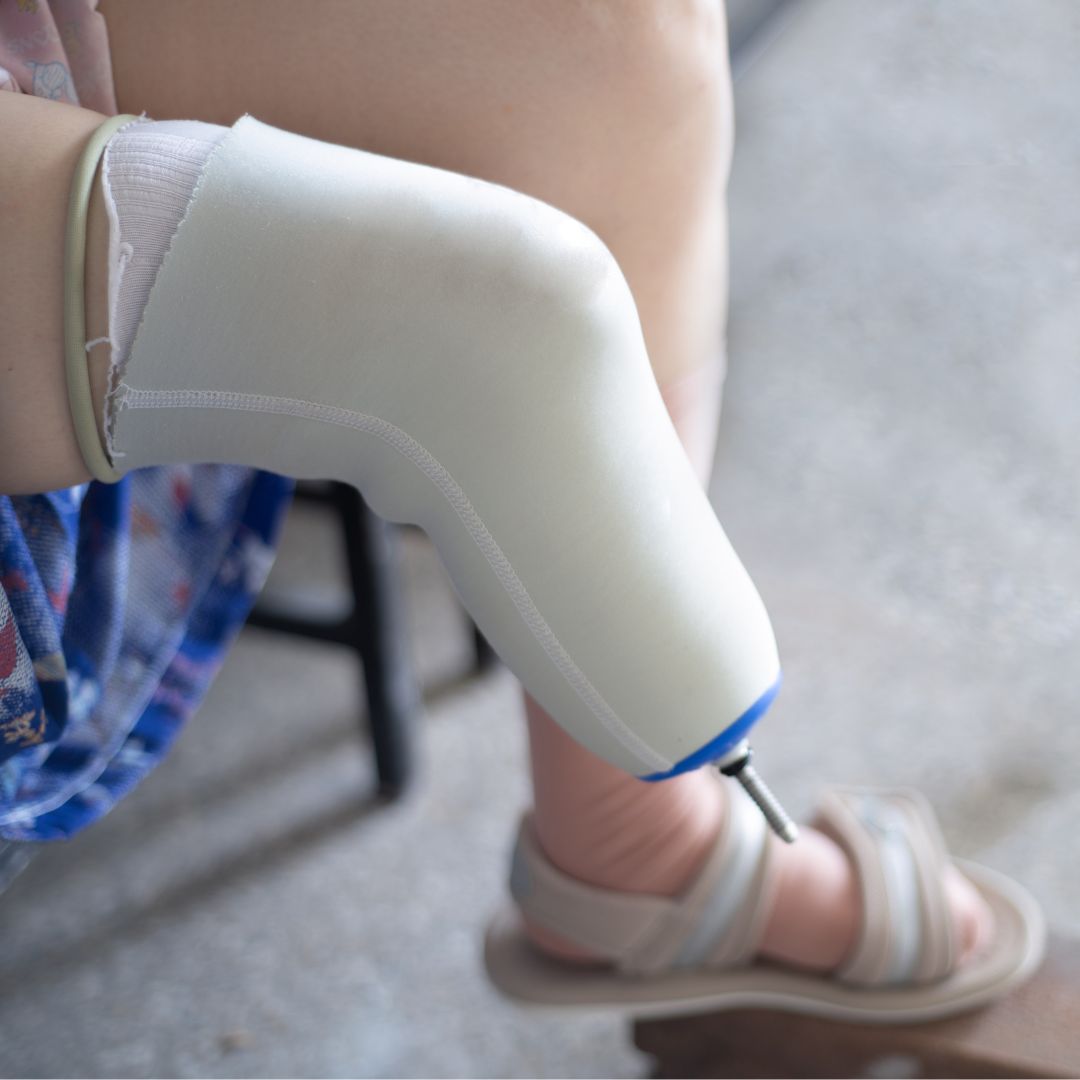
Edema Reduction and Limb Shaping: Immediately after surgery, swelling (edema) is common. Compression helps to reduce this swelling, which is crucial for pain management and preparing the limb for a prosthetic fitting. Consistent compression also helps to shape the residual limb into a conical form, which is ideal for a comfortable and secure prosthetic fit.
-
Pain Management: By reducing swelling and providing support to the tissues, compression can significantly alleviate post-operative pain and discomfort.
-
Improved Blood Circulation: For diabetic patients, maintaining good circulation is paramount. While compression might seem counterintuitive for circulation, gentle, consistent pressure can actually help move fluid more efficiently, preventing venous pooling and supporting overall blood flow in the remaining tissues.
-
Skin Integrity and Healing: Compression helps to stabilize the soft tissues, which can aid in the healing process of the surgical site. It also protects the skin from external trauma, which is particularly important for diabetic skin, often more fragile and prone to breakdown.
-
Desensitization: Wearing compression garments can help desensitize the residual limb, preparing it for the constant pressure and contact of a prosthetic socket. This can reduce phantom limb sensations and improve comfort.
-
Prevention of Complications: By managing edema and promoting healing, compression therapy helps prevent complications such as skin breakdown, infection, and delayed wound closure.
Choosing the Right Compression for Your Residual Limb
Selecting the appropriate compression garment is key to maximizing its benefits. There are several types available, each designed for specific stages of recovery and limb characteristics:
-
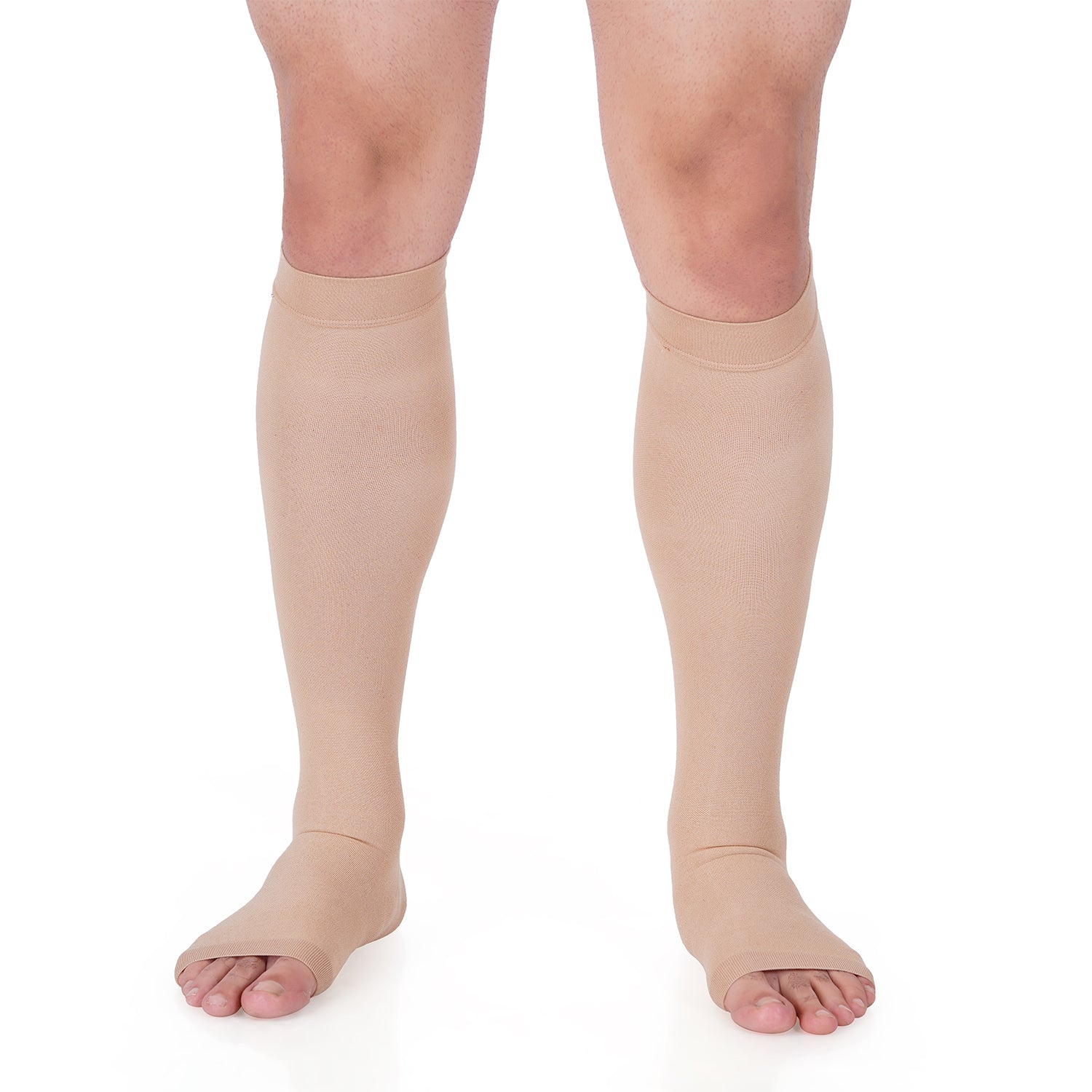
Stump Shrinkers: These are elastic garments, often made of medical-grade silicone or specialized fabrics, designed to apply graduated compression to the residual limb. They are typically worn soon after surgery once the wound has begun to heal, helping to reduce swelling and shape the limb.
-
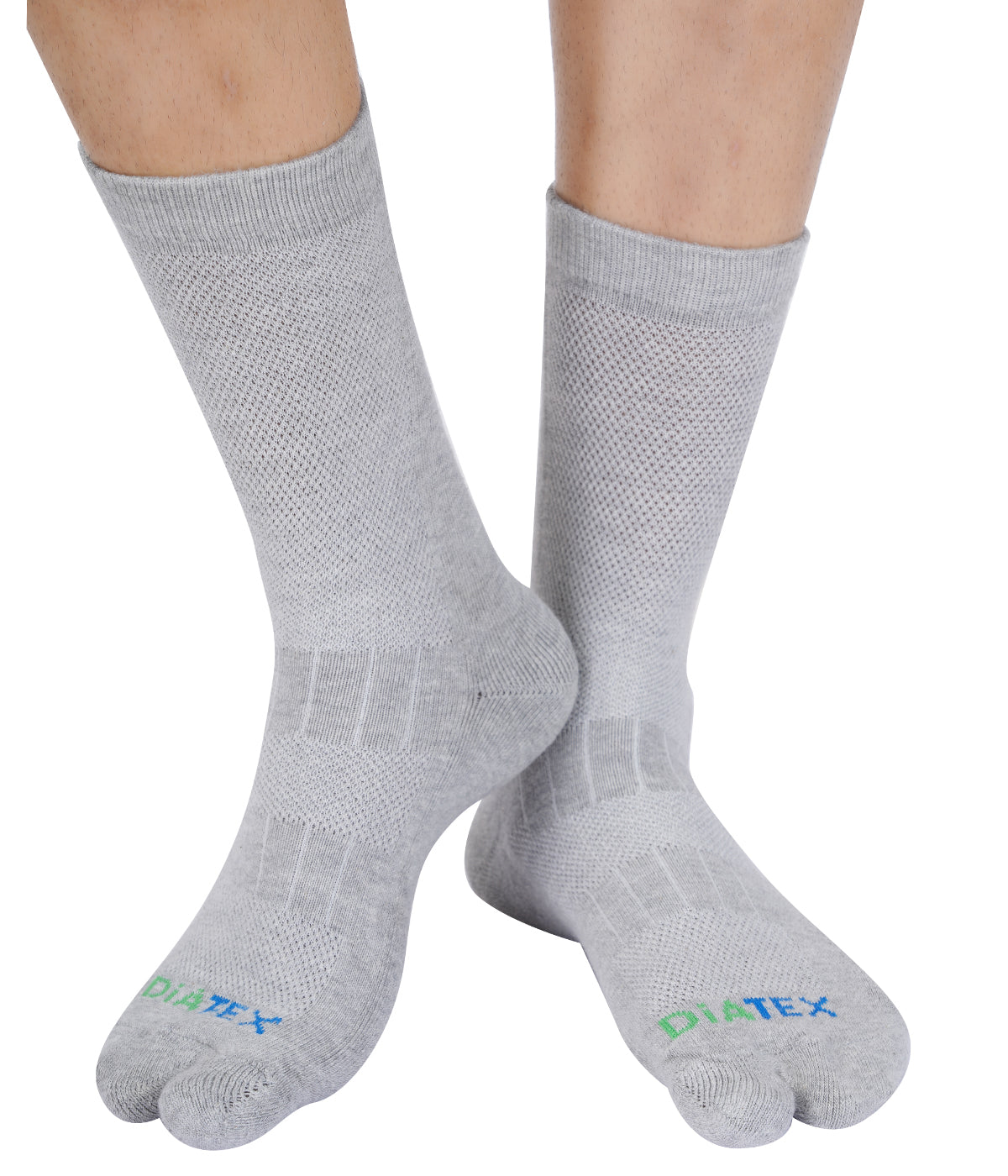
Compression Stockings/Sleeves: While less common for the residual limb itself, compression stockings might be prescribed for the contralateral (non-amputated) leg if there are signs of venous insufficiency or edema.
-
Elastic Bandages: While effective for initial compression, elastic bandages require careful application to ensure even pressure and avoid tourniquet effects, which can be challenging for patients to manage independently. Stump shrinkers offer a more consistent and safer alternative.
Important Considerations:
-
Proper Fit is Crucial: A compression garment that is too tight can impede circulation, while one that is too loose will not provide adequate compression. Professional measurement and fitting by a healthcare provider or a certified prosthetist are essential.
-
Regular Monitoring: The residual limb will change in size and shape during the healing process. Regular monitoring by healthcare professionals is necessary to ensure the compression garment remains effective and to adjust the size as needed.
-
Hygiene: Maintaining strict hygiene of the residual limb and the compression garment is vital to prevent skin irritation and infection, especially for diabetic patients.
-
Compliance: Consistent use of compression therapy as prescribed by healthcare providers is paramount for achieving the best outcomes.
Integrating Compression Therapy into Your Daily Routine
For diabetic patients undergoing amputation, compression therapy isn't just a temporary measure; it's often a long-term commitment that forms a critical part of their daily care routine. By diligently adhering to compression therapy protocols, individuals can significantly improve their comfort, accelerate their rehabilitation, and prepare their residual limb for successful prosthetic use.
Consult with your healthcare team – including your surgeon, prosthetist, and physical therapist – to develop a comprehensive post-amputation care plan that effectively incorporates compression therapy. They can guide you through the selection process, ensure proper fit, and monitor your progress, ultimately empowering you on your journey to recovery and enhanced mobility.
Disclaimer: This blog post is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition.